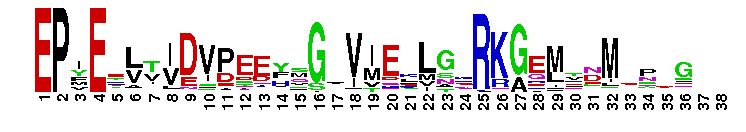| |||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position:  No Conserved Features/Sites Found for BipA_TypA_C No Conserved Features/Sites Found for BipA_TypA_C
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




 BipA_TypA_C: a C-terminal portion of BipA or TypA having homology to the C terminal domains of the elongation factors EF-G and EF-2. A member of the ribosome binding GTPase superfamily, BipA is widely distributed in bacteria and plants. BipA is a highly conserved protein with global regulatory properties in Escherichia coli. BipA is phosphorylated on a tyrosine residue under some cellular conditions. Mutants show altered regulation of some pathways. BipA functions as a translation factor that is required specifically for the expression of the transcriptional modulator Fis. BipA binds to ribosomes at a site that coincides with that of EF-G and has a GTPase activity that is sensitive to high GDP:GTP ratios and, is stimulated by 70S ribosomes programmed with mRNA and aminoacylated tRNAs. The growth rate-dependent induction of BipA allows the efficient expression of Fis, thereby modulating a range of downstream processes, including DNA metabolism and type III secretion.
BipA_TypA_C: a C-terminal portion of BipA or TypA having homology to the C terminal domains of the elongation factors EF-G and EF-2. A member of the ribosome binding GTPase superfamily, BipA is widely distributed in bacteria and plants. BipA is a highly conserved protein with global regulatory properties in Escherichia coli. BipA is phosphorylated on a tyrosine residue under some cellular conditions. Mutants show altered regulation of some pathways. BipA functions as a translation factor that is required specifically for the expression of the transcriptional modulator Fis. BipA binds to ribosomes at a site that coincides with that of EF-G and has a GTPase activity that is sensitive to high GDP:GTP ratios and, is stimulated by 70S ribosomes programmed with mRNA and aminoacylated tRNAs. The growth rate-dependent induction of BipA allows the efficient expression of Fis, thereby modulating a range of downstream processes, including DNA metabolism and type III secretion. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.