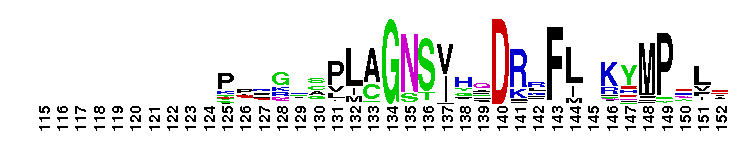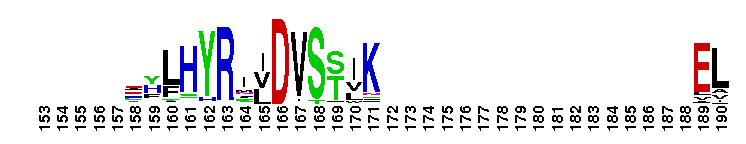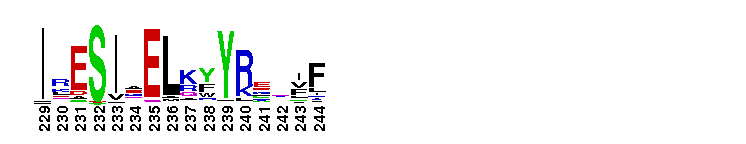| |||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




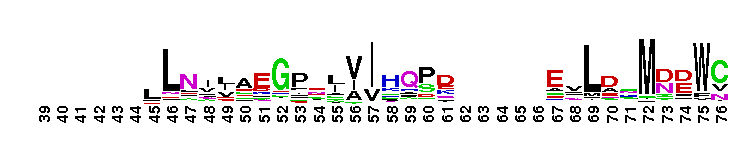
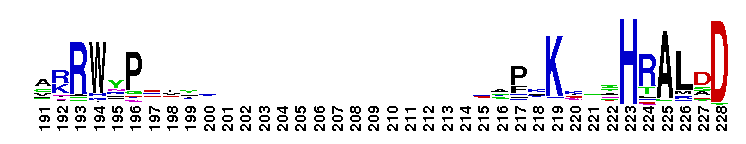
 DEDDh 3'-5' exonuclease domain of oligoribonuclease and similar proteins. Oligoribonuclease (Orn) is a DEDDh-type DnaQ-like 3'-5' exoribonuclease that is responsible for degrading small oligoribonucleotides to mononucleotides. It contains three conserved sequence motifs termed ExoI, ExoII and ExoIII, with a specific Hx(4)D conserved pattern at ExoIII. These motifs are clustered around the active site and contain four conserved acidic residues that serve as ligands for the two metal ions required for catalysis. Orn is essential for Escherichia coli survival. The human homolog, also called Sfn (small fragment nuclease), is able to hydrolyze short single-stranded RNA and DNA oligomers. It plays a role in cellular nucleotide recycling.
DEDDh 3'-5' exonuclease domain of oligoribonuclease and similar proteins. Oligoribonuclease (Orn) is a DEDDh-type DnaQ-like 3'-5' exoribonuclease that is responsible for degrading small oligoribonucleotides to mononucleotides. It contains three conserved sequence motifs termed ExoI, ExoII and ExoIII, with a specific Hx(4)D conserved pattern at ExoIII. These motifs are clustered around the active site and contain four conserved acidic residues that serve as ligands for the two metal ions required for catalysis. Orn is essential for Escherichia coli survival. The human homolog, also called Sfn (small fragment nuclease), is able to hydrolyze short single-stranded RNA and DNA oligomers. It plays a role in cellular nucleotide recycling. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.