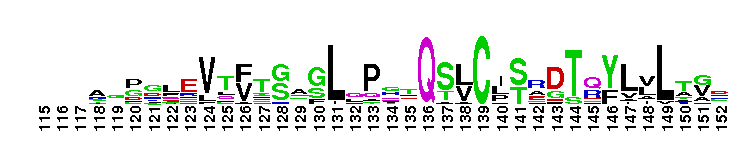| ||||||||||||||||||||
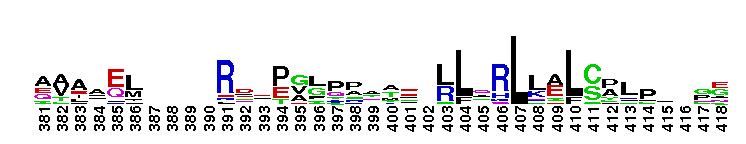
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position:  No Conserved Features/Sites Found for AMH_N No Conserved Features/Sites Found for AMH_N
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




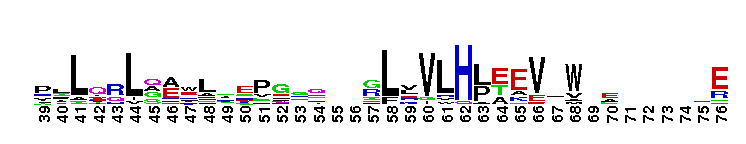
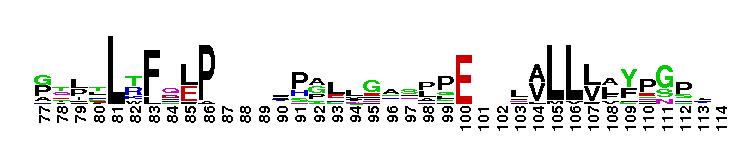
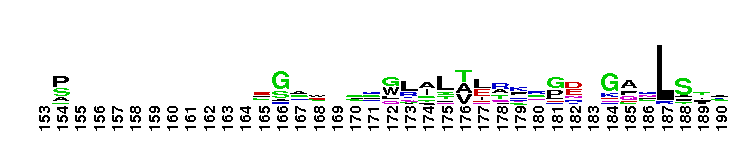
 Anti-Mullerian hormone, N terminal region. Anti-Mullerian hormone, AMH is a signalling molecule involved in male and female sexual differentiation. Defects in synthesis or action of AMH cause persistent Mullerian duct syndrome (PMDS), a rare form of male pseudohermaphroditism. This family represents the N terminal part of the protein, which is not thought to be essential for activity. AMH contains a TGF-beta domain (pfam00019), at the C terminus.
Anti-Mullerian hormone, N terminal region. Anti-Mullerian hormone, AMH is a signalling molecule involved in male and female sexual differentiation. Defects in synthesis or action of AMH cause persistent Mullerian duct syndrome (PMDS), a rare form of male pseudohermaphroditism. This family represents the N terminal part of the protein, which is not thought to be essential for activity. AMH contains a TGF-beta domain (pfam00019), at the C terminus. No pairwise interactions found for the domain AMH_N
No pairwise interactions found for the domain AMH_N