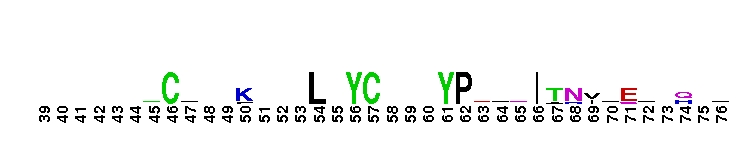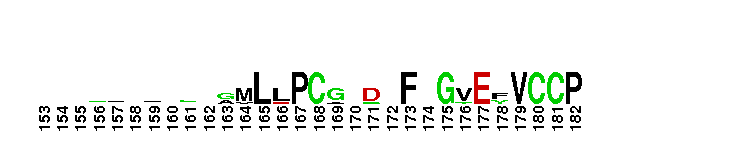| |||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position:  No Conserved Features/Sites Found for APP_N No Conserved Features/Sites Found for APP_N
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




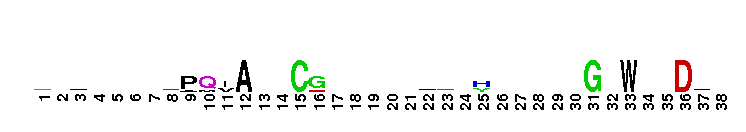
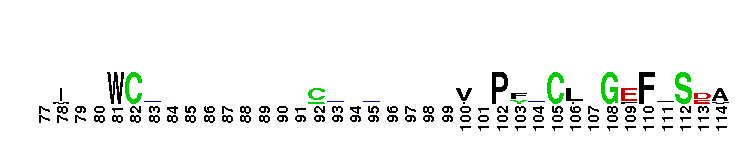
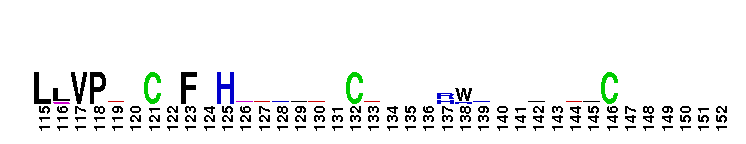
 Amyloid A4 N-terminal heparin-binding. This N-terminal domain of APP, amyloid precursor protein, is the heparin-binding domain of the protein. this region is also responsible for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. The structure reveals both a highly charged basic surface that may interact with glycosaminoglycans in the brain and an abutting hydrophobic surface that is proposed to play an important functional role such as in dimerisation or ligand-binding. Structural similarities with cysteine-rich growth factors, taken together with its known growth-promoting properties, suggest the APP N-terminal domain could function as a growth factor in vivo.
Amyloid A4 N-terminal heparin-binding. This N-terminal domain of APP, amyloid precursor protein, is the heparin-binding domain of the protein. this region is also responsible for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. The structure reveals both a highly charged basic surface that may interact with glycosaminoglycans in the brain and an abutting hydrophobic surface that is proposed to play an important functional role such as in dimerisation or ligand-binding. Structural similarities with cysteine-rich growth factors, taken together with its known growth-promoting properties, suggest the APP N-terminal domain could function as a growth factor in vivo. No pairwise interactions found for the domain APP_N
No pairwise interactions found for the domain APP_N