| ||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




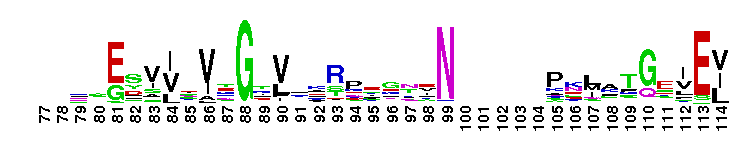
 Asp_Lys_Asn_RS_N: N-terminal, anticodon recognition domain of class 2b aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs). This domain is a beta-barrel domain (OB fold) involved in binding the tRNA anticodon stem-loop. Class 2b aaRSs include the homodimeric aspartyl-, asparaginyl-, and lysyl-tRNA synthetases (AspRS, AsnRS, and LysRS). aaRSs catalyze the specific attachment of amino acids (AAs) to their cognate tRNAs during protein biosynthesis. This 2-step reaction involves i) the activation of the AA by ATP in the presence of magnesium ions, followed by ii) the transfer of the activated AA to the terminal ribose of tRNA. In the case of the class2b aaRSs, the activated AA is attached to the 3'OH of the terminal ribose. Eukaryotes contain 2 sets of aaRSs, both of which are encoded by the nuclear genome. One set concerns with cytoplasmic protein synthesis, whereas the other exclusively with mitochondrial protein synthesis. Included in this group are archeal and archeal-like AspRSs which are non-discriminating and can charge both tRNAAsp and tRNAAsn. E. coli cells have two isoforms of LysRSs (LysS and LysU) encoded by two distinct genes, which are differentially regulated. The cytoplasmic and the mitochondrial isoforms of human LysRS are encoded by a single gene. Yeast cytoplasmic and mitochondrial LysRSs participate in mitochondrial import of cytoplasmic tRNAlysCUU. In addition to their housekeeping role, human LysRS may function as a signaling molecule that activates immune cells. Tomato LysRS may participate in a process possibly connected to conditions of oxidative-stress conditions or heavy metal uptake. It is known that human tRNAlys and LysRS are specifically packaged into HIV-1 suggesting a role for LysRS in tRNA packaging. AsnRS is immunodominant antigen of the filarial nematode Brugia malayai and is of interest as a target for anti-parasitic drug design. Human AsnRS has been shown to be a pro-inflammatory chemokine which interacts with CCR3 chemokine receptors on T cells, immature dendritic cells and macrophages.
Asp_Lys_Asn_RS_N: N-terminal, anticodon recognition domain of class 2b aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs). This domain is a beta-barrel domain (OB fold) involved in binding the tRNA anticodon stem-loop. Class 2b aaRSs include the homodimeric aspartyl-, asparaginyl-, and lysyl-tRNA synthetases (AspRS, AsnRS, and LysRS). aaRSs catalyze the specific attachment of amino acids (AAs) to their cognate tRNAs during protein biosynthesis. This 2-step reaction involves i) the activation of the AA by ATP in the presence of magnesium ions, followed by ii) the transfer of the activated AA to the terminal ribose of tRNA. In the case of the class2b aaRSs, the activated AA is attached to the 3'OH of the terminal ribose. Eukaryotes contain 2 sets of aaRSs, both of which are encoded by the nuclear genome. One set concerns with cytoplasmic protein synthesis, whereas the other exclusively with mitochondrial protein synthesis. Included in this group are archeal and archeal-like AspRSs which are non-discriminating and can charge both tRNAAsp and tRNAAsn. E. coli cells have two isoforms of LysRSs (LysS and LysU) encoded by two distinct genes, which are differentially regulated. The cytoplasmic and the mitochondrial isoforms of human LysRS are encoded by a single gene. Yeast cytoplasmic and mitochondrial LysRSs participate in mitochondrial import of cytoplasmic tRNAlysCUU. In addition to their housekeeping role, human LysRS may function as a signaling molecule that activates immune cells. Tomato LysRS may participate in a process possibly connected to conditions of oxidative-stress conditions or heavy metal uptake. It is known that human tRNAlys and LysRS are specifically packaged into HIV-1 suggesting a role for LysRS in tRNA packaging. AsnRS is immunodominant antigen of the filarial nematode Brugia malayai and is of interest as a target for anti-parasitic drug design. Human AsnRS has been shown to be a pro-inflammatory chemokine which interacts with CCR3 chemokine receptors on T cells, immature dendritic cells and macrophages. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.