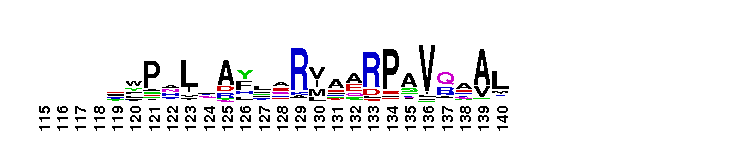| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




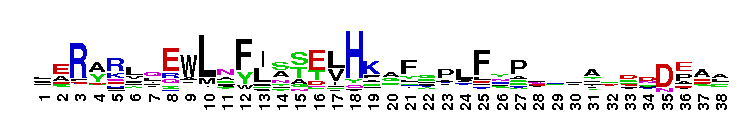
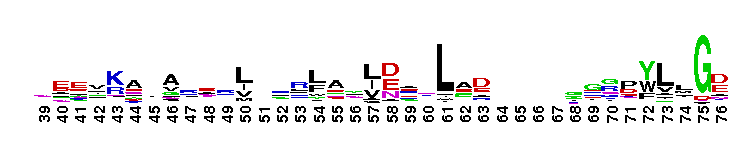
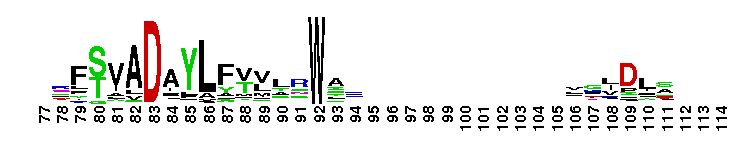
 C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Class Beta Glutathione S-transferases. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Class Beta subfamily; GSTs are cytosolic dimeric proteins involved in cellular detoxification by catalyzing the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) with a wide range of endogenous and xenobiotic alkylating agents, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins, and products of oxidative stress. The GST fold contains an N-terminal thioredoxin-fold domain and a C-terminal alpha helical domain, with an active site located in a cleft between the two domains. GSH binds to the N-terminal domain while the hydrophobic substrate occupies a pocket in the C-terminal domain. Unlike mammalian GSTs which detoxify a broad range of compounds, the bacterial class Beta GSTs exhibit GSH conjugating activity with a narrow range of substrates. In addition to GSH conjugation, they are involved in the protection against oxidative stress and are able to bind antibiotics and reduce the antimicrobial activity of beta-lactam drugs, contributing to antibiotic resistance. The structure of the Proteus mirabilis enzyme reveals that the cysteine in the active site forms a covalent bond with GSH. One member of this subfamily is a GST from Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 that is encoded by the bphK gene and is part of the biphenyl catabolic pathway.
C-terminal, alpha helical domain of Class Beta Glutathione S-transferases. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) C-terminal domain family, Class Beta subfamily; GSTs are cytosolic dimeric proteins involved in cellular detoxification by catalyzing the conjugation of glutathione (GSH) with a wide range of endogenous and xenobiotic alkylating agents, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins, and products of oxidative stress. The GST fold contains an N-terminal thioredoxin-fold domain and a C-terminal alpha helical domain, with an active site located in a cleft between the two domains. GSH binds to the N-terminal domain while the hydrophobic substrate occupies a pocket in the C-terminal domain. Unlike mammalian GSTs which detoxify a broad range of compounds, the bacterial class Beta GSTs exhibit GSH conjugating activity with a narrow range of substrates. In addition to GSH conjugation, they are involved in the protection against oxidative stress and are able to bind antibiotics and reduce the antimicrobial activity of beta-lactam drugs, contributing to antibiotic resistance. The structure of the Proteus mirabilis enzyme reveals that the cysteine in the active site forms a covalent bond with GSH. One member of this subfamily is a GST from Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 that is encoded by the bphK gene and is part of the biphenyl catabolic pathway. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.