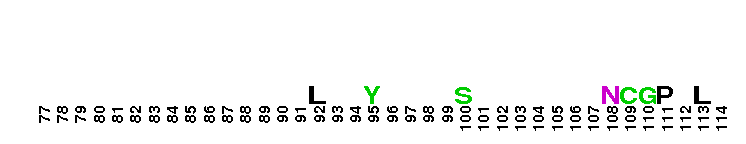| |||||||||||||||||||
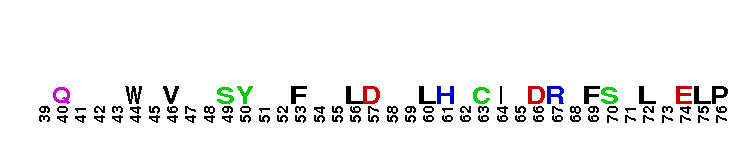
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




 The phosphoinositide binding Phox Homology domain of PX-RICS-like proteins. The PX domain is a phosphoinositide (PI) binding module present in many proteins with diverse functions such as cell signaling, vesicular trafficking, protein sorting, and lipid modification, among others. Members of this family include PX-RICS, TCGAP (Tc10/Cdc42 GTPase-activating protein), and similar proteins. They contain N-terminal PX and Src Homology 3 (SH3) domains, a central Rho GAP domain, and C-terminal extensions. They act as Rho GTPase-activating proteins. PX-RICS is the main isoform expressed during neural development. It is involved in neural functions including axon and dendrite extension, postnatal remodeling, and fine-tuning of neural circuits during early brain development. The PX domain of PX-RICS specifically binds phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P), PI4P, and PI5P. TCGAP is widely expressed in the brain where it is involved in regulating the outgrowth of axons and dendrites and is regulated by the protein tyrosine kinase Fyn. The PX domain is involved in targeting of proteins to PI-enriched membranes, and may also be involved in protein-protein interaction.
The phosphoinositide binding Phox Homology domain of PX-RICS-like proteins. The PX domain is a phosphoinositide (PI) binding module present in many proteins with diverse functions such as cell signaling, vesicular trafficking, protein sorting, and lipid modification, among others. Members of this family include PX-RICS, TCGAP (Tc10/Cdc42 GTPase-activating protein), and similar proteins. They contain N-terminal PX and Src Homology 3 (SH3) domains, a central Rho GAP domain, and C-terminal extensions. They act as Rho GTPase-activating proteins. PX-RICS is the main isoform expressed during neural development. It is involved in neural functions including axon and dendrite extension, postnatal remodeling, and fine-tuning of neural circuits during early brain development. The PX domain of PX-RICS specifically binds phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P), PI4P, and PI5P. TCGAP is widely expressed in the brain where it is involved in regulating the outgrowth of axons and dendrites and is regulated by the protein tyrosine kinase Fyn. The PX domain is involved in targeting of proteins to PI-enriched membranes, and may also be involved in protein-protein interaction. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.