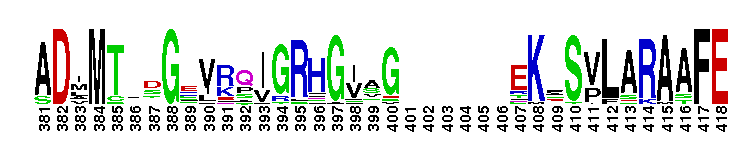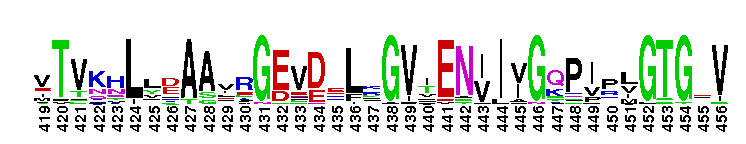| |||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




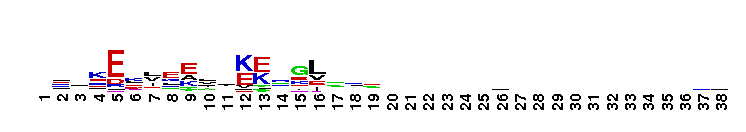
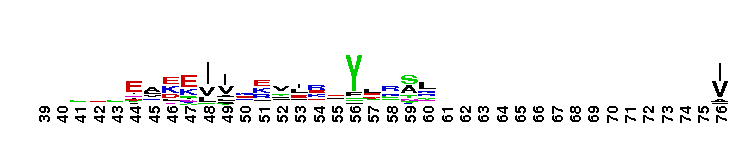
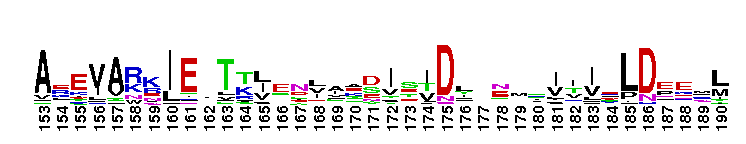
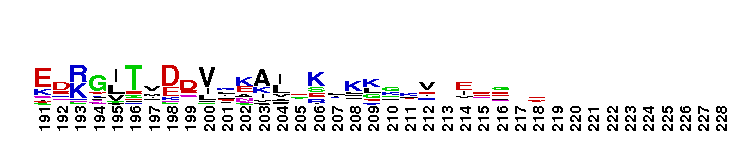
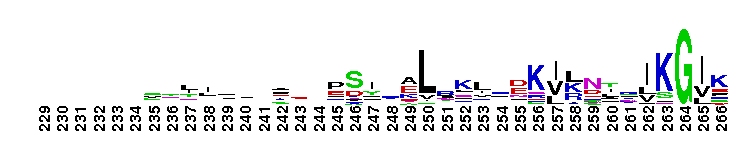
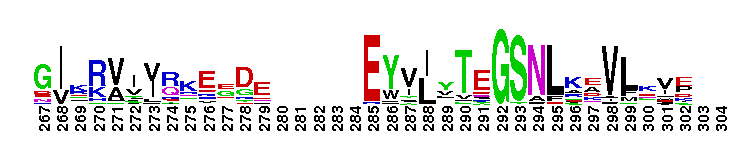
 A'' subunit of Archaeal RNA Polymerase (RNAP). Archaeal RNA polymerase (RNAP), like bacterial RNAP, is a large multi-subunit complex responsible for the synthesis of all RNAs in the cell. The relative positioning of the RNAP core is highly conserved between archaeal RNAP and the three classes of eukaryotic RNAPs. In archaea, the largest subunit is split into two polypeptides, A' and A'', which are encoded by separate genes in an operon. Sequence alignments reveal that the archaeal A'' subunit corresponds to the C-terminal one-third of the RNAPII largest subunit (Rpb1). In subunit A'', several loops in the jaw domain are shorter. The RNAPII Rpb1 interacts with the second-largest subunit (Rpb2) to form the DNA entry and RNA exit channels in addition to the catalytic center of RNA synthesis.
A'' subunit of Archaeal RNA Polymerase (RNAP). Archaeal RNA polymerase (RNAP), like bacterial RNAP, is a large multi-subunit complex responsible for the synthesis of all RNAs in the cell. The relative positioning of the RNAP core is highly conserved between archaeal RNAP and the three classes of eukaryotic RNAPs. In archaea, the largest subunit is split into two polypeptides, A' and A'', which are encoded by separate genes in an operon. Sequence alignments reveal that the archaeal A'' subunit corresponds to the C-terminal one-third of the RNAPII largest subunit (Rpb1). In subunit A'', several loops in the jaw domain are shorter. The RNAPII Rpb1 interacts with the second-largest subunit (Rpb2) to form the DNA entry and RNA exit channels in addition to the catalytic center of RNA synthesis. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.