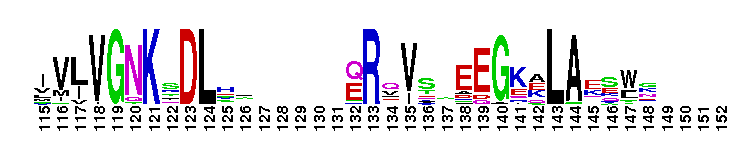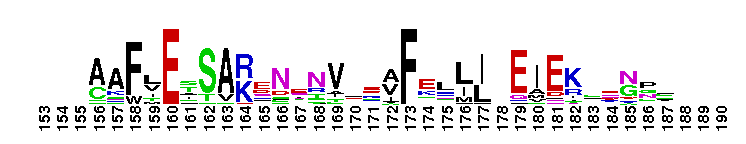| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




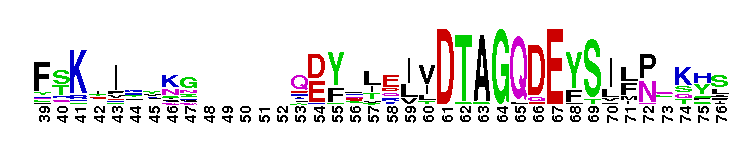
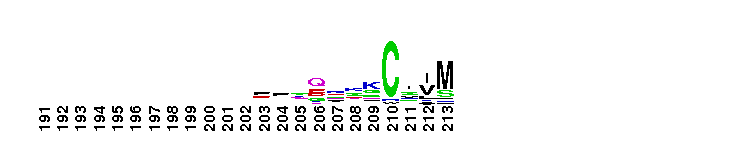
 Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain (RheB) is a small GTPase. Rheb (Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain) subfamily. Rheb was initially identified in rat brain, where its expression is elevated by seizures or by long-term potentiation. It is expressed ubiquitously, with elevated levels in muscle and brain. Rheb functions as an important mediator between the tuberous sclerosis complex proteins, TSC1 and TSC2, and the mammalian target of rapamycin (TOR) kinase to stimulate cell growth. TOR kinase regulates cell growth by controlling nutrient availability, growth factors, and the energy status of the cell. TSC1 and TSC2 form a dimeric complex that has tumor suppressor activity, and TSC2 is a GTPase activating protein (GAP) for Rheb. The TSC1/TSC2 complex inhibits the activation of TOR kinase through Rheb. Rheb has also been shown to induce the formation of large cytoplasmic vacuoles in a process that is dependent on the GTPase cycle of Rheb, but independent of the TOR kinase, suggesting Rheb plays a role in endocytic trafficking that leads to cell growth and cell-cycle progression. Most Ras proteins contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with a typical sequence motif CaaX, where a = an aliphatic amino acid and X = any amino acid. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Ras proteins.
Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain (RheB) is a small GTPase. Rheb (Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain) subfamily. Rheb was initially identified in rat brain, where its expression is elevated by seizures or by long-term potentiation. It is expressed ubiquitously, with elevated levels in muscle and brain. Rheb functions as an important mediator between the tuberous sclerosis complex proteins, TSC1 and TSC2, and the mammalian target of rapamycin (TOR) kinase to stimulate cell growth. TOR kinase regulates cell growth by controlling nutrient availability, growth factors, and the energy status of the cell. TSC1 and TSC2 form a dimeric complex that has tumor suppressor activity, and TSC2 is a GTPase activating protein (GAP) for Rheb. The TSC1/TSC2 complex inhibits the activation of TOR kinase through Rheb. Rheb has also been shown to induce the formation of large cytoplasmic vacuoles in a process that is dependent on the GTPase cycle of Rheb, but independent of the TOR kinase, suggesting Rheb plays a role in endocytic trafficking that leads to cell growth and cell-cycle progression. Most Ras proteins contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with a typical sequence motif CaaX, where a = an aliphatic amino acid and X = any amino acid. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Ras proteins. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.