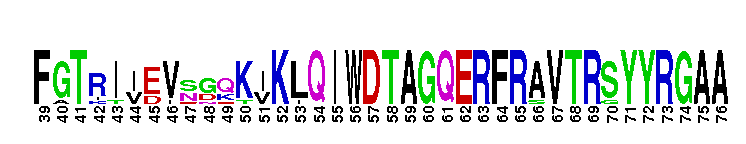| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




 Rab GTPase family 14 (Rab14). Rab14 GTPases are localized to biosynthetic compartments, including the rough ER, the Golgi complex, and the trans-Golgi network, and to endosomal compartments, including early endosomal vacuoles and associated vesicles. Rab14 is believed to function in both the biosynthetic and recycling pathways between the Golgi and endosomal compartments. Rab14 has also been identified on GLUT4 vesicles, and has been suggested to help regulate GLUT4 translocation. In addition, Rab14 is believed to play a role in the regulation of phagocytosis. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) interact with GTP-bound Rab and accelerate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) interact with GDP-bound Rabs to promote the formation of the GTP-bound state. Rabs are further regulated by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which facilitate Rab recycling by masking C-terminal lipid binding and promoting cytosolic localization. Most Rab GTPases contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with sequence motifs CC, CXC, or CCX. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rab proteins. Due to the presence of truncated sequences in this CD, the lipid modification site is not available for annotation.
Rab GTPase family 14 (Rab14). Rab14 GTPases are localized to biosynthetic compartments, including the rough ER, the Golgi complex, and the trans-Golgi network, and to endosomal compartments, including early endosomal vacuoles and associated vesicles. Rab14 is believed to function in both the biosynthetic and recycling pathways between the Golgi and endosomal compartments. Rab14 has also been identified on GLUT4 vesicles, and has been suggested to help regulate GLUT4 translocation. In addition, Rab14 is believed to play a role in the regulation of phagocytosis. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) interact with GTP-bound Rab and accelerate the hydrolysis of GTP to GDP. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) interact with GDP-bound Rabs to promote the formation of the GTP-bound state. Rabs are further regulated by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which facilitate Rab recycling by masking C-terminal lipid binding and promoting cytosolic localization. Most Rab GTPases contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with sequence motifs CC, CXC, or CCX. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rab proteins. Due to the presence of truncated sequences in this CD, the lipid modification site is not available for annotation. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.