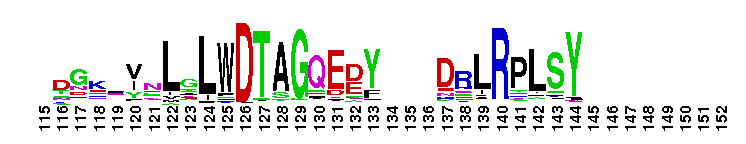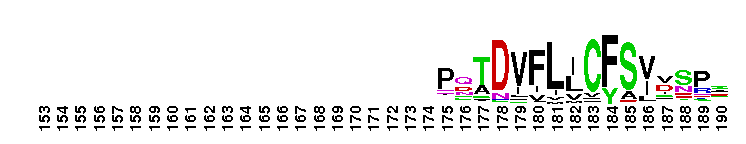| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
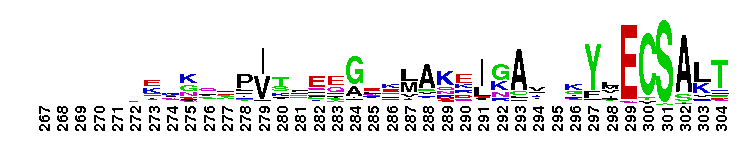
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




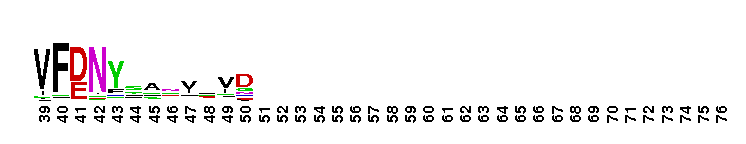
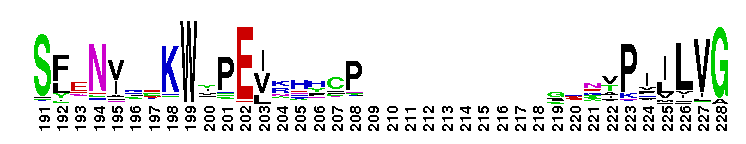
 Ras homology family (Rho) of small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). Members of the Rho (Ras homology) family include RhoA, Cdc42, Rac, Rnd, Wrch1, RhoBTB, and Rop. There are 22 human Rho family members identified currently. These proteins are all involved in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in response to external stimuli. They also have roles in cell transformation by Ras in cytokinesis, in focal adhesion formation and in the stimulation of stress-activated kinase. These various functions are controlled through distinct effector proteins and mediated through a GTP-binding/GTPase cycle involving three classes of regulating proteins: GAPs (GTPase-activating proteins), GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factors), and GDIs (guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors). Most Rho proteins contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with a typical sequence motif CaaX, where a = an aliphatic amino acid and X = any amino acid. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rho proteins. Since crystal structures often lack C-terminal residues, this feature is not available for annotation in many of the CDs in the hierarchy.
Ras homology family (Rho) of small guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases). Members of the Rho (Ras homology) family include RhoA, Cdc42, Rac, Rnd, Wrch1, RhoBTB, and Rop. There are 22 human Rho family members identified currently. These proteins are all involved in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in response to external stimuli. They also have roles in cell transformation by Ras in cytokinesis, in focal adhesion formation and in the stimulation of stress-activated kinase. These various functions are controlled through distinct effector proteins and mediated through a GTP-binding/GTPase cycle involving three classes of regulating proteins: GAPs (GTPase-activating proteins), GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factors), and GDIs (guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors). Most Rho proteins contain a lipid modification site at the C-terminus, with a typical sequence motif CaaX, where a = an aliphatic amino acid and X = any amino acid. Lipid binding is essential for membrane attachment, a key feature of most Rho proteins. Since crystal structures often lack C-terminal residues, this feature is not available for annotation in many of the CDs in the hierarchy. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.