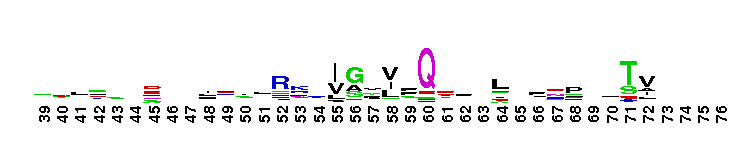| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
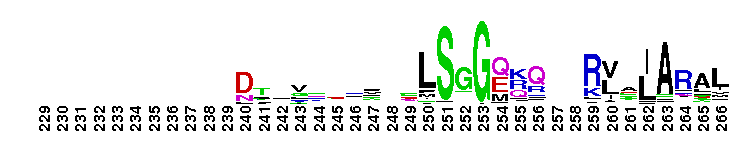
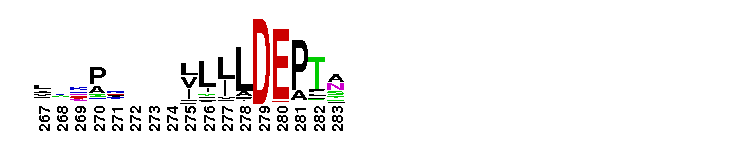
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position:  No Conserved Features/Sites Found for ABC_tran No Conserved Features/Sites Found for ABC_tran
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




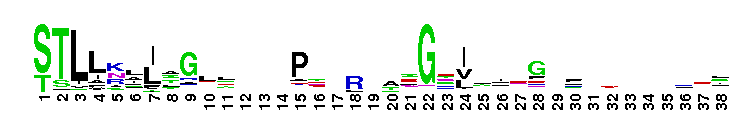
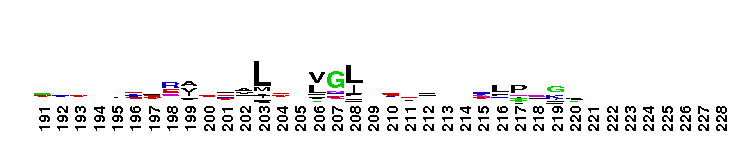
 ABC transporter. ABC transporters for a large family of proteins responsible for translocation of a variety of compounds across biological membranes. ABC transporters are the largest family of proteins in many completely sequenced bacteria. ABC transporters are composed of two copies of this domain and two copies of a transmembrane domain pfam00664. These four domains may belong to a single polypeptide as in human CFTR, or belong in different polypeptide chains.
ABC transporter. ABC transporters for a large family of proteins responsible for translocation of a variety of compounds across biological membranes. ABC transporters are the largest family of proteins in many completely sequenced bacteria. ABC transporters are composed of two copies of this domain and two copies of a transmembrane domain pfam00664. These four domains may belong to a single polypeptide as in human CFTR, or belong in different polypeptide chains. No pairwise interactions found for the domain ABC_tran
No pairwise interactions found for the domain ABC_tran