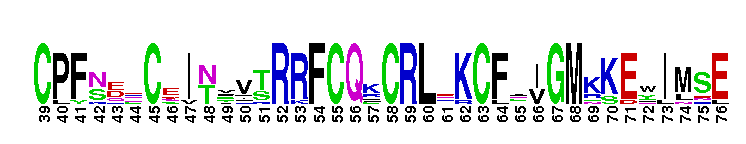| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




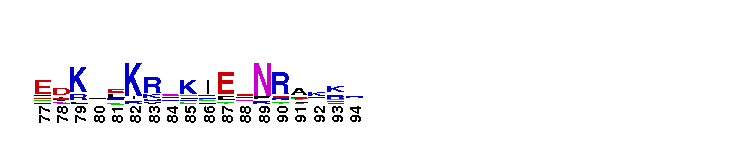
 DNA-binding domain of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is composed of two C4-type zinc fingers. DNA-binding domain (DBD) of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is composed of two C4-type zinc fingers. Each zinc finger contains a group of four Cys residues which co-ordinates a single zinc atom. CAR DBD interacts with CAR response element, a perfect repeat of two AGTTCA motifs with a 4 bp spacer upstream of the target gene, and modulates the rate of transcriptional initiation. The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is a ligand-regulated transcription factor that responds to a diverse array of chemically distinct ligands, including many endogenous compounds and clinical drugs. It functions as a heterodimer with RXR. The CAR/RXR heterodimer binds many common response elements in the promoter regions of a diverse set of target genes involved in the metabolism, transport, and ultimately, elimination of these molecules from the body. CAR is a closest mammalian relative of PXR and is activated by some of the same ligands as PXR and regulates a subset of common genes. The sequence homology and functional similarity suggests that the CAR gene arose from a duplication of an ancestral PXR gene. Like other nuclear receptors, CAR has a central well conserved DNA binding domain, a variable N-terminal domain, a flexible hinge and a C-terminal ligand binding domain.
DNA-binding domain of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is composed of two C4-type zinc fingers. DNA-binding domain (DBD) of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is composed of two C4-type zinc fingers. Each zinc finger contains a group of four Cys residues which co-ordinates a single zinc atom. CAR DBD interacts with CAR response element, a perfect repeat of two AGTTCA motifs with a 4 bp spacer upstream of the target gene, and modulates the rate of transcriptional initiation. The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) is a ligand-regulated transcription factor that responds to a diverse array of chemically distinct ligands, including many endogenous compounds and clinical drugs. It functions as a heterodimer with RXR. The CAR/RXR heterodimer binds many common response elements in the promoter regions of a diverse set of target genes involved in the metabolism, transport, and ultimately, elimination of these molecules from the body. CAR is a closest mammalian relative of PXR and is activated by some of the same ligands as PXR and regulates a subset of common genes. The sequence homology and functional similarity suggests that the CAR gene arose from a duplication of an ancestral PXR gene. Like other nuclear receptors, CAR has a central well conserved DNA binding domain, a variable N-terminal domain, a flexible hinge and a C-terminal ligand binding domain. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.