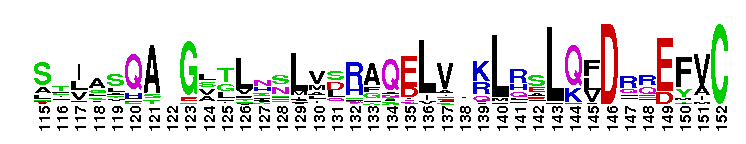| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




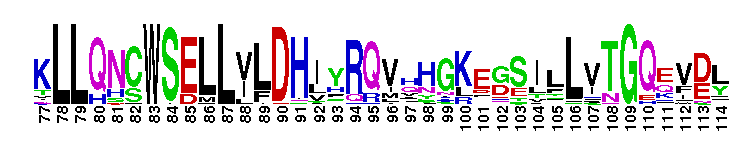
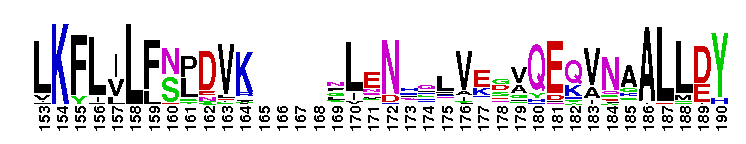
 The ligand binding domain of FTZ-F1 like nuclear receptors. The ligand binding domain of FTZ-F1 like nuclear receptors: This nuclear receptor family includes at least three subgroups of receptors that function in embryo development and differentiation, and other processes. FTZ-F1 interacts with the cis-acting DNA motif of ftz gene, which required at several stages of development. Particularly, FTZ-F1 genes are strongly linked to steroid biosynthesis and sex-determination; LRH-1 is a regulator of bile-acid homeostasis, steroidogenesis, reverse cholesterol transport and the initial stages of embryonic development. SF-1 is an essential regulator of endocrine development and function and is considered a master regulator of reproduction; SF-1 functions cooperatively with other transcription factors to modulate gene expression. Phospholipids have been identified as potential ligand for LRH-1 and steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1). However, the ligand for FTZ-F1 has not yet been identified. Most nuclear receptors function as homodimer or heterodimers. However, LRH-1 and SF-1 bind to DNA as a monomer. Like other members of the nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors, receptors in this family have a central well conserved DNA binding domain (DBD), a variable N-terminal domain, a flexible hinge and a C-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD).
The ligand binding domain of FTZ-F1 like nuclear receptors. The ligand binding domain of FTZ-F1 like nuclear receptors: This nuclear receptor family includes at least three subgroups of receptors that function in embryo development and differentiation, and other processes. FTZ-F1 interacts with the cis-acting DNA motif of ftz gene, which required at several stages of development. Particularly, FTZ-F1 genes are strongly linked to steroid biosynthesis and sex-determination; LRH-1 is a regulator of bile-acid homeostasis, steroidogenesis, reverse cholesterol transport and the initial stages of embryonic development. SF-1 is an essential regulator of endocrine development and function and is considered a master regulator of reproduction; SF-1 functions cooperatively with other transcription factors to modulate gene expression. Phospholipids have been identified as potential ligand for LRH-1 and steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1). However, the ligand for FTZ-F1 has not yet been identified. Most nuclear receptors function as homodimer or heterodimers. However, LRH-1 and SF-1 bind to DNA as a monomer. Like other members of the nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors, receptors in this family have a central well conserved DNA binding domain (DBD), a variable N-terminal domain, a flexible hinge and a C-terminal ligand binding domain (LBD). No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.