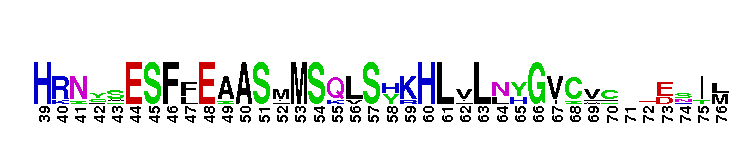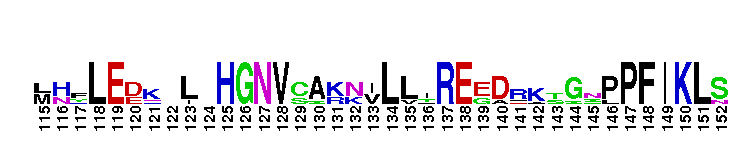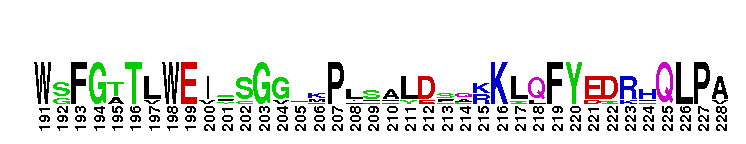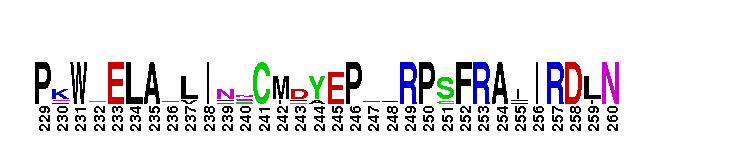ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, RESPONSE TO TYROS ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, RESPONSE TO TYROS
|
 ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC
|
 AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 19 AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 19
|
 B CELL-POSITIVE, NK CELL-NEGATIVE B CELL-POSITIVE, NK CELL-NEGATIVE
|
 BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1
|
 CATARACT 6, AGE-RELATED CORTICAL CATARACT 6, AGE-RELATED CORTICAL
|
 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD
|
 COLON CANCER, SOMATIC COLON CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 CROUZON SYNDROME CROUZON SYNDROME
|
 DEFICIENCY DEFICIENCY
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, INSULIN-RESISTANT, WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS DIABETES MELLITUS, INSULIN-RESISTANT, WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT DIABETES MELLITUS, NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT
|
 FG SYNDROME 4 FG SYNDROME 4
|
 GASTRIC CANCER, SOMATIC GASTRIC CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR, FAMILIAL GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR, FAMILIAL
|
 GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR, SOMATIC GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR, SOMATIC
|
 GERM CELL TUMOR, SOMATIC GERM CELL TUMOR, SOMATIC
|
 GLIOBLASTOMA, SOMATIC GLIOBLASTOMA, SOMATIC
|
 HARTSFIELD SYNDROME HARTSFIELD SYNDROME
|
 HEMANGIOMA, CAPILLARY INFANTILE, SOMATIC HEMANGIOMA, CAPILLARY INFANTILE, SOMATIC
|
 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CHILDHOOD TYPE, SOMATIC HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CHILDHOOD TYPE, SOMATIC
|
 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 1 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 1
|
 HYPERINSULINEMIC HYPOGLYCEMIA, FAMILIAL, 5 HYPERINSULINEMIC HYPOGLYCEMIA, FAMILIAL, 5
|
 HYPOCHONDROPLASIA HYPOCHONDROPLASIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 IN IN
|
 INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN, CONGENITAL, WITH ANHIDROSIS INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN, CONGENITAL, WITH ANHIDROSIS
|
 INSULIN RESISTANCE INSULIN RESISTANCE
|
 INSULIN RESISTANCE, INCLUDED INSULIN RESISTANCE, INCLUDED
|
 IRAK4 DEFICIENCY IRAK4 DEFICIENCY
|
 LADD SYNDROME LADD SYNDROME
|
 LEUKEMIA, ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC, SOMATIC, INCLUDED LEUKEMIA, ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 LEUKEMIA, ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA, ACUTE MYELOID
|
 LEUKEMIA, ACUTE MYELOID, SOMATIC LEUKEMIA, ACUTE MYELOID, SOMATIC
|
 LEUKEMIA, PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME-POSITIVE, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB LEUKEMIA, PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME-POSITIVE, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB
|
 LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, I LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, I
|
 LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, IA LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, IA
|
 LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC
|
 LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE SYNDROME 1 LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE SYNDROME 1
|
 MALFORMATIONS MALFORMATIONS
|
 MAST CELL DISEASE, SYSTEMIC MAST CELL DISEASE, SYSTEMIC
|
 MAST CELL LEUKEMIA MAST CELL LEUKEMIA
|
 MASTOCYTOSIS WITH ASSOCIATED HEMATOLOGIC DISORDER, INCLUDED;; MASTOCYTOSIS WITH ASSOCIATED HEMATOLOGIC DISORDER, INCLUDED;;
|
 MASTOCYTOSIS, ADULT SPORADIC, INCLUDE MASTOCYTOSIS, ADULT SPORADIC, INCLUDE
|
 MASTOCYTOSIS, SPORADIC, CHILDHOOD-ONSET MASTOCYTOSIS, SPORADIC, CHILDHOOD-ONSET
|
 MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS
|
 MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIA MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIA
|
 MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIB MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIB
|
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 MYASTHENIC SYNDROME, CONGENITAL, ASSOCIATED WITH ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTOR MYASTHENIC SYNDROME, CONGENITAL, ASSOCIATED WITH ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTOR
|
 NEUROBLASTOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 3 NEUROBLASTOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 3
|
 NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II
|
 NONSMALL CELL LUNG CANCER, RESISTANCE TO TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR NONSMALL CELL LUNG CANCER, RESISTANCE TO TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR
|
 NONSMALL CELL LUNG CANCER, RESPONSE TO TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR IN, NONSMALL CELL LUNG CANCER, RESPONSE TO TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR IN,
|
 NOONAN SYNDROME 7 NOONAN SYNDROME 7
|
 OBESITY, HYPERPHAGIA, AND DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY OBESITY, HYPERPHAGIA, AND DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY
|
 OVARIAN CANCER, SOMATIC OVARIAN CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
|
 PFEIFFER SYNDROME PFEIFFER SYNDROME
|
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, INCLUDED PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, INCLUDED
|
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, SOMATIC, IN PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, SOMATIC, IN
|
 PIEBALDISM PIEBALDISM
|
 PIEBALDISM WITH SENSORINEURAL DEAFNESS PIEBALDISM WITH SENSORINEURAL DEAFNESS
|
 PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF
|
 RENAL AGENESIS RENAL AGENESIS
|
 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1
|
 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1, SOMATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1, SOMATIC
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 38 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 38
|
 SADDAN DYSPLASIA SADDAN DYSPLASIA
|
 SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED
|
 SELECTIVE T-CELL DEFECT SELECTIVE T-CELL DEFECT
|
 SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNODEFICIENCY, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE, T CELL-NEGATIVE, SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNODEFICIENCY, AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE, T CELL-NEGATIVE,
|
 SOMATIC SOMATIC
|
 SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5
|
 SPONDYLOMETAEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, SHORT LIMB-HAND TYPE SPONDYLOMETAEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, SHORT LIMB-HAND TYPE
|
 T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;| THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;|
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, SPORADIC MEDULLARY, INCLUDED;; THYROID CARCINOMA, SPORADIC MEDULLARY, INCLUDED;;
|
 TO TO
|
 VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE
|
 VENOUS MALFORMATIONS, MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS AND MUCOSAL VENOUS MALFORMATIONS, MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS AND MUCOSAL
|






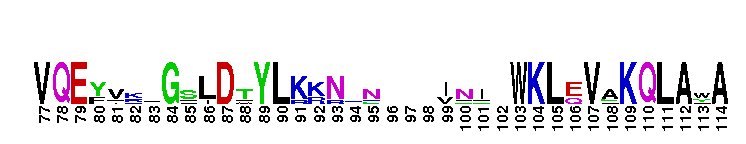
 Pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Janus kinases 2 and 3. Protein Tyrosine Kinase (PTK) family; Janus kinase 2 (Jak2) and Jak3; pseudokinase domain (repeat 1). The PTKc (catalytic domain) family to which this subfamily belongs, is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases such as protein serine/threonine kinases, RIO kinases, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). PTKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to tyrosine (tyr) residues in protein substrates. Jak2 and Jak3 are members of the Janus kinase (Jak) subfamily of proteins, which are cytoplasmic (or nonreceptor) tyr kinases containing an N-terminal FERM domain, followed by a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, a pseudokinase domain, and a C-terminal tyr kinase domain. The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to tyr kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity and ATP binding. It modulates the kinase activity of the C-terminal catalytic domain. Jaks are crucial for cytokine receptor signaling. They are activated by autophosphorylation upon cytokine-induced receptor aggregation, and subsequently trigger downstream signaling events such as the phosphorylation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs). Jak2 is widely expressed in many tissues while Jak3 is expressed only in hematopoietic cells. Jak2 is essential for the signaling of hormone-like cytokines such as growth hormone, erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, and prolactin, as well as some IFNs and cytokines that signal through the IL-3 and gp130 receptors. Jak3 binds the shared receptor subunit common gamma chain and thus, is essential in the signaling of cytokines that use it such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. Disruption of Jak2 in mice results in an embryonic lethal phenotype with multiple defects including erythropoietic and cardiac abnormalities. It is the only Jak gene that results in a lethal phenotype when disrupted in mice. A mutation in the pseudokinase domain of Jak2, V617F, is present in many myeloproliferative diseases, including almost all patients with polycythemia vera, and 50% of patients with essential thrombocytosis and myelofibrosis. Jak3 is important in lymphoid development and myeloid cell differentiation. Inactivating mutations in Jak3 have been reported in humans with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
Pseudokinase (repeat 1) domain of the Protein Tyrosine Kinases, Janus kinases 2 and 3. Protein Tyrosine Kinase (PTK) family; Janus kinase 2 (Jak2) and Jak3; pseudokinase domain (repeat 1). The PTKc (catalytic domain) family to which this subfamily belongs, is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other kinases such as protein serine/threonine kinases, RIO kinases, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K). PTKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to tyrosine (tyr) residues in protein substrates. Jak2 and Jak3 are members of the Janus kinase (Jak) subfamily of proteins, which are cytoplasmic (or nonreceptor) tyr kinases containing an N-terminal FERM domain, followed by a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, a pseudokinase domain, and a C-terminal tyr kinase domain. The pseudokinase domain shows similarity to tyr kinases but lacks crucial residues for catalytic activity and ATP binding. It modulates the kinase activity of the C-terminal catalytic domain. Jaks are crucial for cytokine receptor signaling. They are activated by autophosphorylation upon cytokine-induced receptor aggregation, and subsequently trigger downstream signaling events such as the phosphorylation of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs). Jak2 is widely expressed in many tissues while Jak3 is expressed only in hematopoietic cells. Jak2 is essential for the signaling of hormone-like cytokines such as growth hormone, erythropoietin, thrombopoietin, and prolactin, as well as some IFNs and cytokines that signal through the IL-3 and gp130 receptors. Jak3 binds the shared receptor subunit common gamma chain and thus, is essential in the signaling of cytokines that use it such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21. Disruption of Jak2 in mice results in an embryonic lethal phenotype with multiple defects including erythropoietic and cardiac abnormalities. It is the only Jak gene that results in a lethal phenotype when disrupted in mice. A mutation in the pseudokinase domain of Jak2, V617F, is present in many myeloproliferative diseases, including almost all patients with polycythemia vera, and 50% of patients with essential thrombocytosis and myelofibrosis. Jak3 is important in lymphoid development and myeloid cell differentiation. Inactivating mutations in Jak3 have been reported in humans with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.