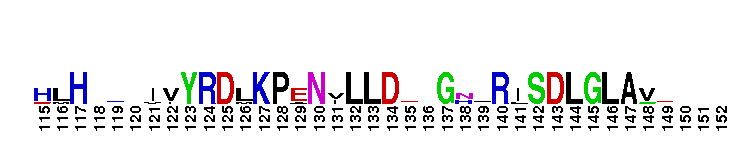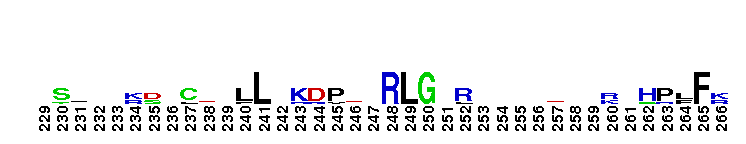ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC
|
 AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 19 AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 19
|
 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7
|
 BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4
|
 CATARACT 6, AGE-RELATED CORTICAL CATARACT 6, AGE-RELATED CORTICAL
|
 CEREBRAL INFARCTION, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CEREBRAL INFARCTION, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 CROUZON SYNDROME CROUZON SYNDROME
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, INSULIN-RESISTANT, WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS DIABETES MELLITUS, INSULIN-RESISTANT, WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT DIABETES MELLITUS, NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II
|
 ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA
|
 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2
|
 FG SYNDROME 4 FG SYNDROME 4
|
 FIBRODYSPLASIA OSSIFICANS PROGRESSIVA FIBRODYSPLASIA OSSIFICANS PROGRESSIVA
|
 GASTRIC CANCER, SOMATIC GASTRIC CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 GLIOBLASTOMA, SOMATIC GLIOBLASTOMA, SOMATIC
|
 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC
|
 HARTSFIELD SYNDROME HARTSFIELD SYNDROME
|
 HEMANGIOMA, CAPILLARY INFANTILE, SOMATIC HEMANGIOMA, CAPILLARY INFANTILE, SOMATIC
|
 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CHILDHOOD TYPE, SOMATIC HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CHILDHOOD TYPE, SOMATIC
|
 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 1 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 1
|
 HYPERINSULINEMIC HYPOGLYCEMIA, FAMILIAL, 5 HYPERINSULINEMIC HYPOGLYCEMIA, FAMILIAL, 5
|
 HYPOCHONDROPLASIA HYPOCHONDROPLASIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN, CONGENITAL, WITH ANHIDROSIS INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN, CONGENITAL, WITH ANHIDROSIS
|
 INSULIN RESISTANCE INSULIN RESISTANCE
|
 INSULIN RESISTANCE, INCLUDED INSULIN RESISTANCE, INCLUDED
|
 IRAK4 DEFICIENCY IRAK4 DEFICIENCY
|
 JUVENILE POLYPOSIS SYNDROME JUVENILE POLYPOSIS SYNDROME
|
 LADD SYNDROME LADD SYNDROME
|
 LOEYS-DIETZ SYNDROME, TYPE 1A LOEYS-DIETZ SYNDROME, TYPE 1A
|
 LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, I LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, I
|
 LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, IA LYMPHEDEMA, HEREDITARY, IA
|
 LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC
|
 LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE SYNDROME 1 LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE SYNDROME 1
|
 MALFORMATIONS MALFORMATIONS
|
 MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME
|
 MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS
|
 MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIA MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIA
|
 MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIB MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIB
|
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 MULTIPLE SELF-HEALING SQUAMOUS EPITHELIOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO MULTIPLE SELF-HEALING SQUAMOUS EPITHELIOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 NEUROBLASTOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 3 NEUROBLASTOMA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 3
|
 NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II
|
 NOONAN SYNDROME 7 NOONAN SYNDROME 7
|
 OBESITY, HYPERPHAGIA, AND DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY OBESITY, HYPERPHAGIA, AND DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY
|
 OGUCHI DISEASE 2 OGUCHI DISEASE 2
|
 OVARIAN CANCER, SOMATIC OVARIAN CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
|
 PERSISTENT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME, TYPE II PERSISTENT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME, TYPE II
|
 PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME
|
 PFEIFFER SYNDROME PFEIFFER SYNDROME
|
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, INCLUDED PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, INCLUDED
|
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, SOMATIC, IN PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, SOMATIC, IN
|
 PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF
|
 RENAL AGENESIS RENAL AGENESIS
|
 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1
|
 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1, SOMATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1, SOMATIC
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 38 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 38
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62
|
 SADDAN DYSPLASIA SADDAN DYSPLASIA
|
 SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED
|
 SELECTIVE T-CELL DEFECT SELECTIVE T-CELL DEFECT
|
 SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA
|
 SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5
|
 SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA 14 SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA 14
|
 SPONDYLOMETAEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, SHORT LIMB-HAND TYPE SPONDYLOMETAEPIPHYSEAL DYSPLASIA, SHORT LIMB-HAND TYPE
|
 T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC
|
 TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II
|
 THROMBOCYTOPENIA 2 THROMBOCYTOPENIA 2
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;| THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;|
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, SPORADIC MEDULLARY, INCLUDED;; THYROID CARCINOMA, SPORADIC MEDULLARY, INCLUDED;;
|
 TO TO
|
 VENOUS MALFORMATIONS, MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS AND MUCOSAL VENOUS MALFORMATIONS, MULTIPLE CUTANEOUS AND MUCOSAL
|






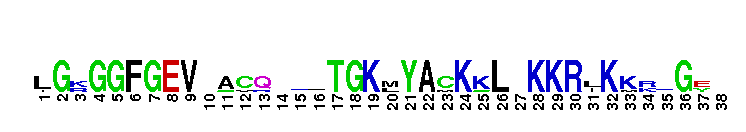
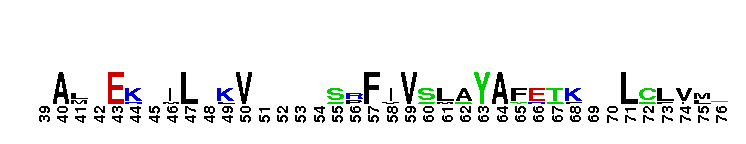
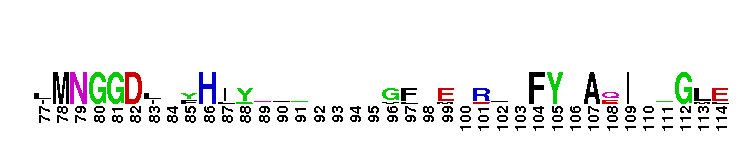
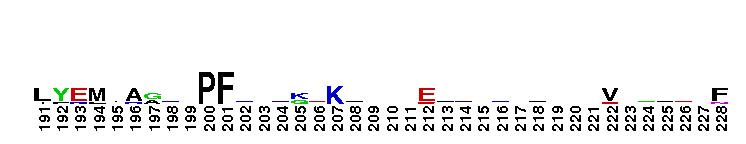
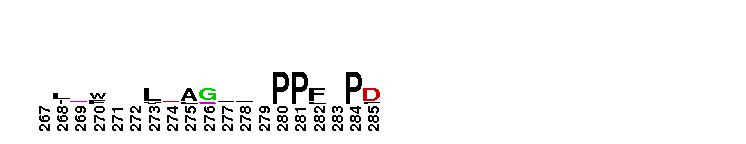
 Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, G protein-coupled Receptor Kinase. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), G protein-coupled Receptor Kinase (GRK) subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The GRK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. GRKs phosphorylate and regulate G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the largest superfamily of cell surface receptors, which regulate some part of nearly all physiological functions. Phosphorylated GPCRs bind to arrestins, which prevents further G protein signaling despite the presence of activating ligand. GRKs contain a central catalytic domain, flanked by N- and C-terminal extensions. The N-terminus contains an RGS (regulator of G protein signaling) homology (RH) domain and several motifs. The C-terminus diverges among different groups of GRKs. There are seven types of GRKs, named GRK1 to GRK7. They are subdivided into three main groups: visual (GRK1/7); beta-adrenergic receptor kinases (GRK2/3); and GRK4-like (GRK4/5/6). Expression of GRK2/3/5/6 is widespread while GRK1/4/7 show a limited tissue distribution. The substrate spectrum of the widely expressed GRKs partially overlaps. GRKs play important roles in the cardiovascular, immune, respiratory, skeletal, and nervous systems.
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, G protein-coupled Receptor Kinase. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), G protein-coupled Receptor Kinase (GRK) subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The GRK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. GRKs phosphorylate and regulate G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), the largest superfamily of cell surface receptors, which regulate some part of nearly all physiological functions. Phosphorylated GPCRs bind to arrestins, which prevents further G protein signaling despite the presence of activating ligand. GRKs contain a central catalytic domain, flanked by N- and C-terminal extensions. The N-terminus contains an RGS (regulator of G protein signaling) homology (RH) domain and several motifs. The C-terminus diverges among different groups of GRKs. There are seven types of GRKs, named GRK1 to GRK7. They are subdivided into three main groups: visual (GRK1/7); beta-adrenergic receptor kinases (GRK2/3); and GRK4-like (GRK4/5/6). Expression of GRK2/3/5/6 is widespread while GRK1/4/7 show a limited tissue distribution. The substrate spectrum of the widely expressed GRKs partially overlaps. GRKs play important roles in the cardiovascular, immune, respiratory, skeletal, and nervous systems. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.