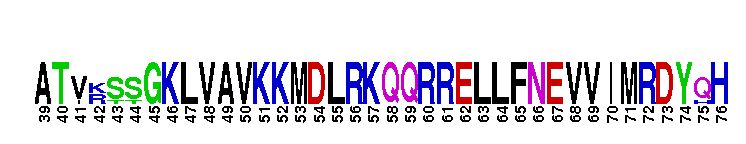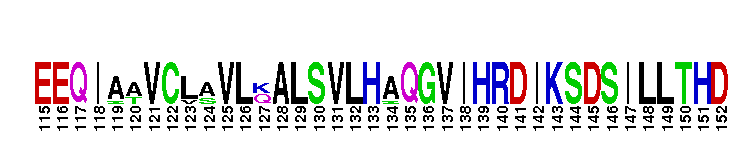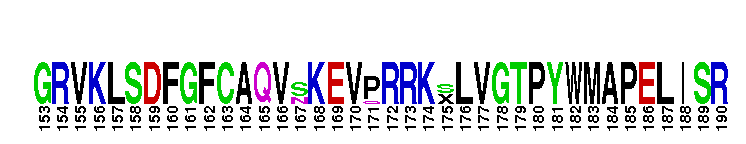ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC
|
 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7
|
 BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4
|
 CATARACT 6, AGE-RELATED CORTICAL CATARACT 6, AGE-RELATED CORTICAL
|
 CEREBRAL INFARCTION, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CEREBRAL INFARCTION, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD
|
 COLON CANCER, SOMATIC COLON CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 CROUZON SYNDROME CROUZON SYNDROME
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, INSULIN-RESISTANT, WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS DIABETES MELLITUS, INSULIN-RESISTANT, WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT DIABETES MELLITUS, NONINSULIN-DEPENDENT
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II
|
 ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA
|
 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2
|
 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 (EIEE2) EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 (EIEE2)
|
 FG SYNDROME 4 FG SYNDROME 4
|
 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC
|
 HARTSFIELD SYNDROME HARTSFIELD SYNDROME
|
 HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CHILDHOOD TYPE, SOMATIC HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA, CHILDHOOD TYPE, SOMATIC
|
 HYPERINSULINEMIC HYPOGLYCEMIA, FAMILIAL, 5 HYPERINSULINEMIC HYPOGLYCEMIA, FAMILIAL, 5
|
 HYPOCHONDROPLASIA HYPOCHONDROPLASIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 INSULIN RESISTANCE INSULIN RESISTANCE
|
 INSULIN RESISTANCE, INCLUDED INSULIN RESISTANCE, INCLUDED
|
 IRAK4 DEFICIENCY IRAK4 DEFICIENCY
|
 LADD SYNDROME LADD SYNDROME
|
 LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC
|
 LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE SYNDROME 1 LYMPHOPROLIFERATIVE SYNDROME 1
|
 MALFORMATIONS MALFORMATIONS
|
 MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME
|
 MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA (MICPCH) MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA (MICPCH)
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS
|
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 NEPHRONOPHTHISIS 9 (NPHP9) NEPHRONOPHTHISIS 9 (NPHP9)
|
 NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II
|
 NOONAN SYNDROME 7 NOONAN SYNDROME 7
|
 OBESITY, HYPERPHAGIA, AND DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY OBESITY, HYPERPHAGIA, AND DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY
|
 OGUCHI DISEASE 2 OGUCHI DISEASE 2
|
 PANCREATIC CANCER, SOMATIC PANCREATIC CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME
|
 PFEIFFER SYNDROME PFEIFFER SYNDROME
|
 PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF
|
 PROSTATE CANCER, SOMATIC PROSTATE CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1
|
 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1, SOMATIC RENAL CELL CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, 1, SOMATIC
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 (RP62) RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 (RP62)
|
 SADDAN DYSPLASIA SADDAN DYSPLASIA
|
 SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED
|
 SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME 2A (SRPS2A) SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME 2A (SRPS2A)
|
 SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA
|
 SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5
|
 SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA 14 SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA 14
|
 T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC
|
 TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II
|
 THROMBOCYTOPENIA 2 THROMBOCYTOPENIA 2
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;| THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;|
|
 TO TO
|






 Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, p21-activated kinase 4. Serine/threonine kinases (STKs), p21-activated kinase (PAK) 4, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The PAK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. PAKs are Rho family GTPase-regulated kinases that serve as important mediators in the function of Cdc42 (cell division cycle 42) and Rac. PAKs from higher eukaryotes are classified into two groups (I and II), according to their biochemical and structural features. PAK4 belongs to group II. Group II PAKs contain a PBD (p21-binding domain) and a C-terminal catalytic domain, but do not harbor an AID (autoinhibitory domain) or SH3 binding sites. PAK4 regulates cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. It is essential for embryonic viability and proper neural development. Mice lacking PAK4 die due to defects in the fetal heart. In addition, their spinal cord motor neurons showed failure to differentiate and migrate. PAK4 also plays a role in cell survival and tumorigenesis. It is overexpressed in many primary tumors including colon, esophageal, and mammary tumors. PAK4 has also been implicated in viral and bacterial infection pathways.
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, p21-activated kinase 4. Serine/threonine kinases (STKs), p21-activated kinase (PAK) 4, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The PAK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. PAKs are Rho family GTPase-regulated kinases that serve as important mediators in the function of Cdc42 (cell division cycle 42) and Rac. PAKs from higher eukaryotes are classified into two groups (I and II), according to their biochemical and structural features. PAK4 belongs to group II. Group II PAKs contain a PBD (p21-binding domain) and a C-terminal catalytic domain, but do not harbor an AID (autoinhibitory domain) or SH3 binding sites. PAK4 regulates cell morphology and cytoskeletal organization. It is essential for embryonic viability and proper neural development. Mice lacking PAK4 die due to defects in the fetal heart. In addition, their spinal cord motor neurons showed failure to differentiate and migrate. PAK4 also plays a role in cell survival and tumorigenesis. It is overexpressed in many primary tumors including colon, esophageal, and mammary tumors. PAK4 has also been implicated in viral and bacterial infection pathways. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.