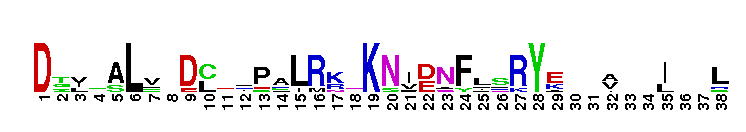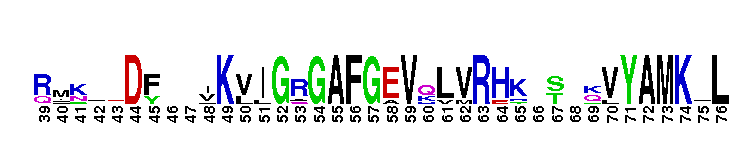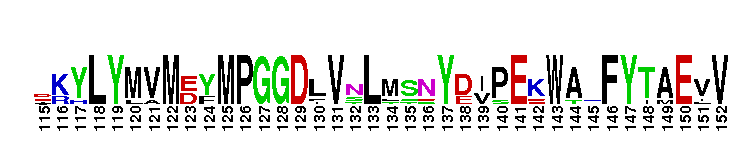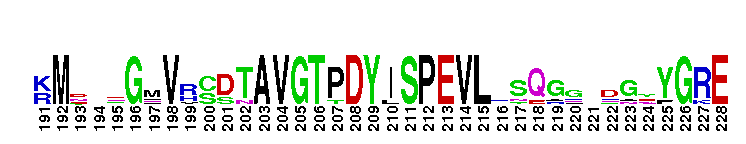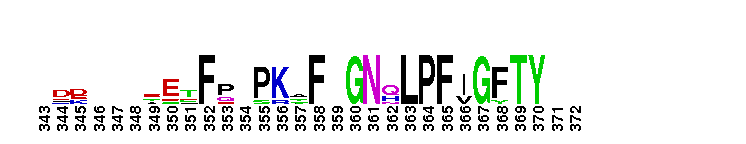| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




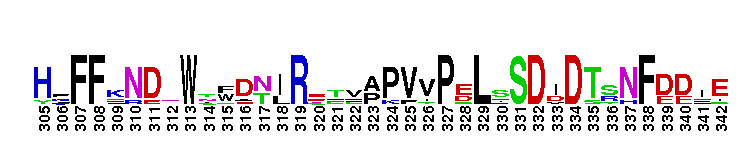
 Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase (ROCK) subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The ROCK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. ROCK is also referred to as Rho-associated kinase or simply as Rho kinase. It contains an N-terminal extension, a catalytic kinase domain, and a long C-terminal extension, which contains a coiled-coil region encompassing a Rho-binding domain (RBD) and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. ROCK is auto-inhibited by the RBD and PH domain interacting with the catalytic domain. It is activated via interaction with Rho GTPases and is involved in many cellular functions including contraction, adhesion, migration, motility, proliferation, and apoptosis. The ROCK subfamily consists of two isoforms, ROCK1 and ROCK2, which may be functionally redundant in some systems, but exhibit different tissue distributions. Both isoforms are ubiquitously expressed in most tissues, but ROCK2 is more prominent in brain and skeletal muscle while ROCK1 is more pronounced in the liver, testes, and kidney. Studies in knockout mice result in different phenotypes, suggesting that the two isoforms do not compensate for each other during embryonic development.
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase (ROCK) subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The ROCK subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. ROCK is also referred to as Rho-associated kinase or simply as Rho kinase. It contains an N-terminal extension, a catalytic kinase domain, and a long C-terminal extension, which contains a coiled-coil region encompassing a Rho-binding domain (RBD) and a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. ROCK is auto-inhibited by the RBD and PH domain interacting with the catalytic domain. It is activated via interaction with Rho GTPases and is involved in many cellular functions including contraction, adhesion, migration, motility, proliferation, and apoptosis. The ROCK subfamily consists of two isoforms, ROCK1 and ROCK2, which may be functionally redundant in some systems, but exhibit different tissue distributions. Both isoforms are ubiquitously expressed in most tissues, but ROCK2 is more prominent in brain and skeletal muscle while ROCK1 is more pronounced in the liver, testes, and kidney. Studies in knockout mice result in different phenotypes, suggesting that the two isoforms do not compensate for each other during embryonic development. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.