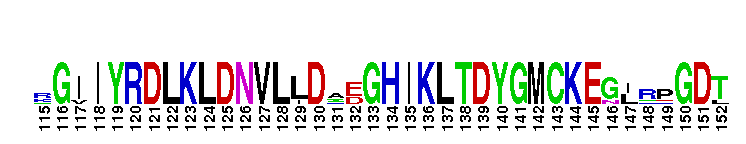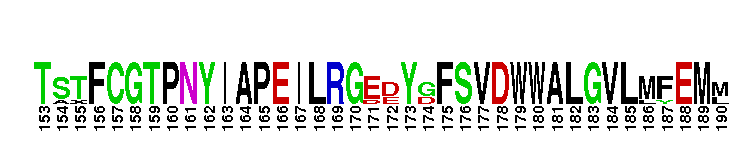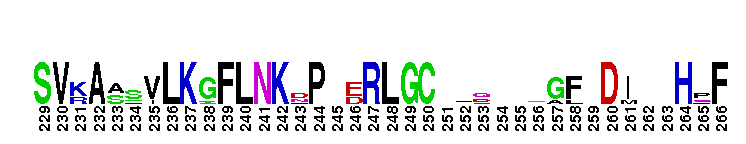ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC ADENOCARCINOMA OF LUNG, SOMATIC
|
 AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 19 AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 19
|
 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7
|
 BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 1
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4
|
 CEREBRAL INFARCTION, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO CEREBRAL INFARCTION, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME, MILD
|
 COLON CANCER, SOMATIC COLON CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; COLORECTAL CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 COWDEN DISEASE 6 COWDEN DISEASE 6
|
 CROUZON SYNDROME CROUZON SYNDROME
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II
|
 ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA
|
 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2
|
 FG SYNDROME 4 FG SYNDROME 4
|
 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC
|
 HARTSFIELD SYNDROME HARTSFIELD SYNDROME
|
 HYPOCHONDROPLASIA HYPOCHONDROPLASIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 LADD SYNDROME LADD SYNDROME
|
 LEUKEMIA, PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME-POSITIVE, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB LEUKEMIA, PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME-POSITIVE, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB
|
 LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC LYMPHOMA, NON-HODGKIN, SOMATIC
|
 MALFORMATIONS MALFORMATIONS
|
 MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME
|
 MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 19
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS
|
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II
|
 NOONAN SYNDROME 7 NOONAN SYNDROME 7
|
 OGUCHI DISEASE 2 OGUCHI DISEASE 2
|
 PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
|
 PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME
|
 PFEIFFER SYNDROME PFEIFFER SYNDROME
|
 PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 38 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 38
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62
|
 SADDAN DYSPLASIA SADDAN DYSPLASIA
|
 SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED
|
 SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA
|
 SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5
|
 SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA 14 SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA 14
|
 T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC
|
 TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II
|
 THROMBOCYTOPENIA 2 THROMBOCYTOPENIA 2
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FOLLICULAR, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;| THYROID CARCINOMA, PAPILLARY, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;|
|
 TO TO
|
 VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE
|






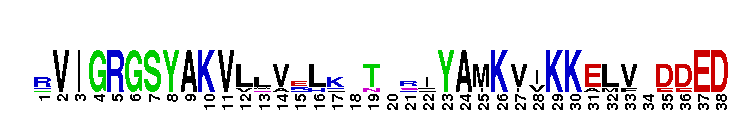
 Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Atypical Protein Kinase C. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), Atypical Protein Kinase C (aPKC) subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The aPKC subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. PKCs are classified into three groups (classical, atypical, and novel) depending on their mode of activation and the structural characteristics of their regulatory domain. aPKCs only require phosphatidylserine (PS) for activation. They contain a C2-like region, instead of a calcium-binding (C2) region found in classical PKCs, in their regulatory domain. There are two aPKC isoforms, zeta and iota. aPKCs are involved in many cellular functions including proliferation, migration, apoptosis, polarity maintenance and cytoskeletal regulation. They also play a critical role in the regulation of glucose metabolism and in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.
Catalytic domain of the Protein Serine/Threonine Kinase, Atypical Protein Kinase C. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), Atypical Protein Kinase C (aPKC) subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The aPKC subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. PKCs are classified into three groups (classical, atypical, and novel) depending on their mode of activation and the structural characteristics of their regulatory domain. aPKCs only require phosphatidylserine (PS) for activation. They contain a C2-like region, instead of a calcium-binding (C2) region found in classical PKCs, in their regulatory domain. There are two aPKC isoforms, zeta and iota. aPKCs are involved in many cellular functions including proliferation, migration, apoptosis, polarity maintenance and cytoskeletal regulation. They also play a critical role in the regulation of glucose metabolism and in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.