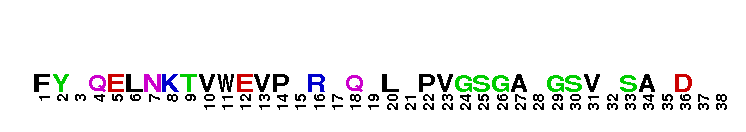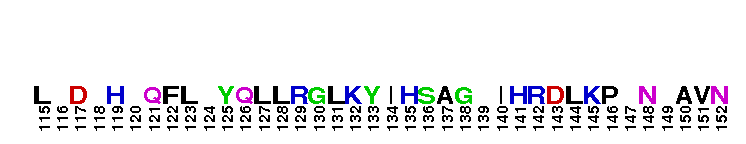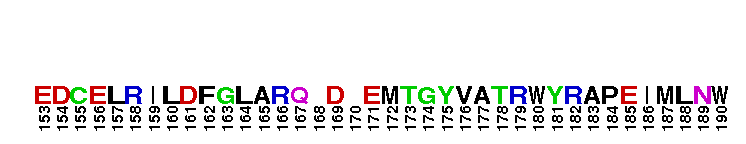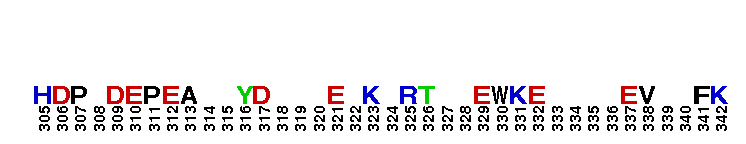AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7 AORTIC ANEURYSM, FAMILIAL THORACIC 7
|
 BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED BLADDER CANCER, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO BREAST CANCER, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME CAMPTODACTYLY, TALL STATURE, AND HEARING LOSS SYNDROME
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 3
|
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME 4
|
 CENTRAL HYPOVENTILATION SYNDROME, CONGENITAL, WITH HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE CENTRAL HYPOVENTILATION SYNDROME, CONGENITAL, WITH HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE
|
 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB
|
 COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME COFFIN-LOWRY SYNDROME
|
 COWDEN DISEASE 6 COWDEN DISEASE 6
|
 CROUZON SYNDROME CROUZON SYNDROME
|
 DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS, TYPE II
|
 ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA ENDOCRINE-CEREBROOSTEODYSPLASIA
|
 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2
|
 EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 (EIEE2) EPILEPTIC ENCEPHALOPATHY, EARLY INFANTILE, 2 (EIEE2)
|
 FG SYNDROME 4 FG SYNDROME 4
|
 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE 9C (GSD9C) GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE 9C (GSD9C)
|
 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXC
|
 HARTSFIELD SYNDROME HARTSFIELD SYNDROME
|
 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 1 HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO, 1
|
 HYPOCHONDROPLASIA HYPOCHONDROPLASIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITH OR WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA
|
 HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO HYPOGONADOTROPIC HYPOGONADISM 2 WITHOUT ANOSMIA, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO
|
 LADD SYNDROME LADD SYNDROME
|
 LEUKEMIA, PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME-POSITIVE, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB LEUKEMIA, PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME-POSITIVE, RESISTANT TO IMATINIB
|
 MALFORMATIONS MALFORMATIONS
|
 MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME MEGALENCEPHALY-POLYMICROGYRIA-POLYDACTYLY-HYDROCEPHALUS SYNDROME
|
 MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC MELANOMA, MALIGNANT, SOMATIC
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA (MICPCH) MENTAL RETARDATION AND MICROCEPHALY WITH PONTINE AND CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA (MICPCH)
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED 30
|
 MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH NYSTAGMUS
|
 MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIA MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIA
|
 MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIB MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE NEOPLASIA, TYPE IIB
|
 MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;; MULTIPLE MYELOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED;;
|
 NEPHRONOPHTHISIS 9 (NPHP9) NEPHRONOPHTHISIS 9 (NPHP9)
|
 NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II NEUROPATHY, HEREDITARY SENSORY, TYPE II
|
 OGUCHI DISEASE 2 OGUCHI DISEASE 2
|
 PANCREATIC CANCER, SOMATIC PANCREATIC CANCER, SOMATIC
|
 PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT PARKINSON DISEASE 8, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
|
 PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME PEUTZ-JEGHERS SYNDROME
|
 PFEIFFER SYNDROME PFEIFFER SYNDROME
|
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, INCLUDED PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, INCLUDED
|
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, SOMATIC, IN PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA, SOMATIC, IN
|
 PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF PROSTATE CANCER, PROGRESSION AND METASTASIS OF
|
 RENAL AGENESIS RENAL AGENESIS
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62
|
 RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 (RP62) RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 62 (RP62)
|
 SADDAN DYSPLASIA SADDAN DYSPLASIA
|
 SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED SCAPHOCEPHALY, MAXILLARY RETRUSION, AND MENTAL RETARDATION, INCLUDED
|
 SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME 2A (SRPS2A) SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME 2A (SRPS2A)
|
 SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA SHORT RIB-POLYDACTYLY SYNDROME, TYPE IIA
|
 SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED SPERMATOCYTIC SEMINOMA, SOMATIC, INCLUDED
|
 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5 SPERMATOGENIC FAILURE 5
|
 T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC T-CELL IMMUNODEFICIENCY, RECURRENT INFECTIONS, AUTOIMMUNITY, AND CARDIAC
|
 TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC TESTICULAR TUMOR, SOMATIC
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE I, INCLUDED
|
 THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II THANATOPHORIC DYSPLASIA, TYPE II
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY, INCLUDED THYROID CARCINOMA, FAMILIAL MEDULLARY, INCLUDED
|
 THYROID CARCINOMA, SPORADIC MEDULLARY, INCLUDED;; THYROID CARCINOMA, SPORADIC MEDULLARY, INCLUDED;;
|
 TO TO
|
 VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE VARIANT OF UNKNOWN SIGNIFICANCE
|






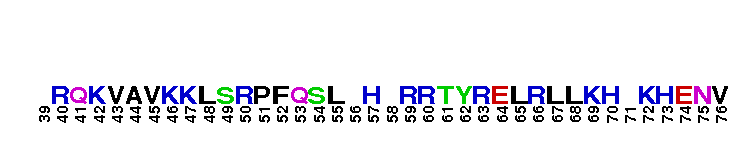
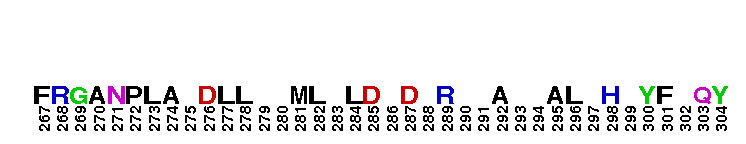
 Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p38beta Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), p38beta subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The p38beta subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. p38 kinases are mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), serving as important mediators of cellular responses to extracellular signals. They are activated by the MAPK kinases MKK3 and MKK6, which in turn are activated by upstream MAPK kinase kinases including TAK1, ASK1, and MLK3, in response to cellular stresses or inflammatory cytokines. Vertebrates contain four isoforms of p38, named alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. p38beta, also called MAPK11, is widely expressed in tissues and shows more similarity with p38alpha than with the other isoforms. Both are sensitive to pyridinylimidazoles and share some common substrates such as MAPK activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) and the transcription factors ATF2, c-Fos and, ELK-1. p38beta is involved in regulating the activation of the cyclooxygenase-2 promoter and the expression of TGFbeta-induced alpha-smooth muscle cell actin.
Catalytic domain of the Serine/Threonine Kinase, p38beta Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. Serine/Threonine Kinases (STKs), p38beta subfamily, catalytic (c) domain. STKs catalyze the transfer of the gamma-phosphoryl group from ATP to serine/threonine residues on protein substrates. The p38beta subfamily is part of a larger superfamily that includes the catalytic domains of other protein STKs, protein tyrosine kinases, RIO kinases, aminoglycoside phosphotransferase, choline kinase, and phosphoinositide 3-kinase. p38 kinases are mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), serving as important mediators of cellular responses to extracellular signals. They are activated by the MAPK kinases MKK3 and MKK6, which in turn are activated by upstream MAPK kinase kinases including TAK1, ASK1, and MLK3, in response to cellular stresses or inflammatory cytokines. Vertebrates contain four isoforms of p38, named alpha, beta, gamma, and delta. p38beta, also called MAPK11, is widely expressed in tissues and shows more similarity with p38alpha than with the other isoforms. Both are sensitive to pyridinylimidazoles and share some common substrates such as MAPK activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) and the transcription factors ATF2, c-Fos and, ELK-1. p38beta is involved in regulating the activation of the cyclooxygenase-2 promoter and the expression of TGFbeta-induced alpha-smooth muscle cell actin. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.