| |||||||||||||||||||
Tips:  Range on the Protein: Protein ID Protein Position Domain Position: 
|
|---|
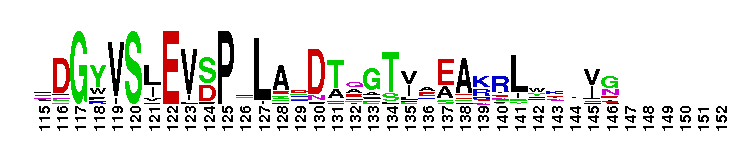
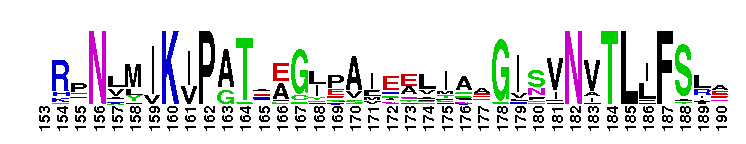
Weblogos are Copyright (c) 2002 Regents of the University of California
| DMDM_info@umbc.edu | 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250 | Department of Biological Sciences | Phone: 410-455-2258 |




 Transaldolase-like proteins from plants and bacteria. Transaldolase-like proteins from plants and bacteria. Transaldolase is found in the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway, that catalyze the reversible transfer of a dihydroxyacetone group from fructose-6-phosphate to erythrose-4-phosphate yielding sedoheptulose-7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. They are members of the class I aldolases, who are characterized by using a Schiff-base mechanism for stabilization of the reaction intermediates.
Transaldolase-like proteins from plants and bacteria. Transaldolase-like proteins from plants and bacteria. Transaldolase is found in the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway, that catalyze the reversible transfer of a dihydroxyacetone group from fructose-6-phosphate to erythrose-4-phosphate yielding sedoheptulose-7-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. They are members of the class I aldolases, who are characterized by using a Schiff-base mechanism for stabilization of the reaction intermediates. No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.
No pairwise interactions are available for this conserved domain.